The Future of STEM Education
STEM education, which stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, has always been a crucial component of the education system, preparing students for the challenges of the modern world. As we look towards the future, the landscape of STEM education is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, changing societal needs, and the increasing demand for skilled professionals in STEM fields. In this article, we will delve into the future of STEM education, exploring its key aspects, potential trends, and the impact it may have on the way we learn and work.
The Shift Towards Personalized Learning

One of the most significant trends shaping the future of STEM education is the shift towards personalized learning. Traditional, one-size-fits-all teaching methods are giving way to a more individualized approach that takes into account students’ unique learning styles, interests, and abilities. With the help of technology, educators are now able to create customized learning experiences for each student, allowing them to progress at their own pace and focus on areas where they need more support.
For example, adaptive learning platforms use data analytics to track students’ progress and adjust the curriculum in real-time based on their performance. This not only helps students stay engaged and motivated but also ensures that they are mastering the concepts effectively. By personalizing the learning experience, educators can better cater to the diverse needs of students and foster a deeper understanding of STEM subjects.
Integration of Emerging Technologies
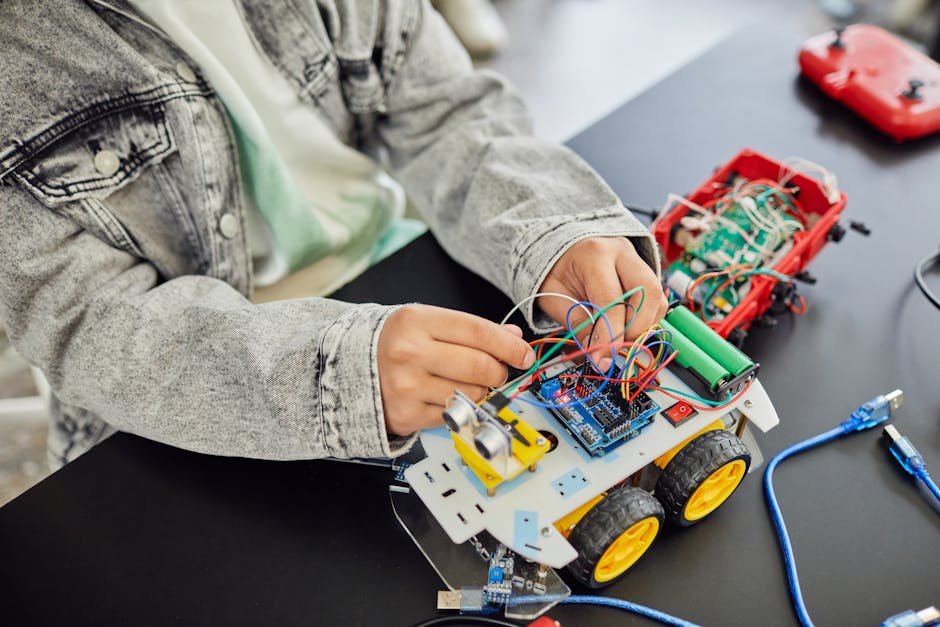
Another key aspect of the future of STEM education is the integration of emerging technologies into the curriculum. As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, it is essential for students to be exposed to the latest tools and resources that are shaping the future of various industries. From artificial intelligence and virtual reality to 3D printing and robotics, incorporating these technologies into STEM education can provide students with hands-on experience and practical skills that are highly sought after in the job market.
For instance, coding has become an essential skill in today’s digital age, and many schools are now introducing coding classes as part of their STEM curriculum. By teaching students how to code, educators are preparing them for careers in software development, cybersecurity, and other technology-related fields. Moreover, by engaging with emerging technologies, students can explore new avenues of innovation and creativity, fostering a spirit of curiosity and exploration.
Emphasis on Real-World Applications

In the future of STEM education, there is a growing emphasis on connecting classroom learning to real-world applications. While theoretical knowledge is essential, it is equally important for students to understand how STEM concepts are applied in practical settings and how they can make a tangible impact on society. By incorporating real-world projects, case studies, and hands-on activities into the curriculum, educators can help students see the relevance of STEM subjects in their everyday lives.
For example, project-based learning is a popular approach that allows students to work on real-world challenges and come up with solutions using STEM principles. By working on projects such as designing sustainable cities, creating renewable energy sources, or developing innovative healthcare technologies, students can see the direct impact of their knowledge and skills. This not only makes learning more engaging and meaningful but also prepares students for the complexities of the real world.
Focus on Diversity and Inclusion

As we look towards the future of STEM education, it is crucial to address the lack of diversity and inclusion in STEM fields. Historically, women, minorities, and other underrepresented groups have been marginalized in STEM-related careers, leading to a lack of diverse perspectives and talents in these fields. To ensure a more equitable and inclusive future, educators are now focusing on promoting diversity and inclusion in STEM education from an early age.
One way to promote diversity in STEM is to provide equal access to resources and opportunities for all students, regardless of their background. This may involve offering scholarships, mentorship programs, and outreach initiatives to encourage underrepresented groups to pursue STEM careers. Additionally, incorporating diverse perspectives and role models into the curriculum can help students see themselves reflected in the field and inspire them to pursue their passions.
Rise of Interdisciplinary Approaches
In the future of STEM education, there is a growing recognition of the importance of interdisciplinary approaches that bridge the gap between different STEM disciplines. While each STEM field has its own unique principles and methodologies, many of the most significant challenges we face today require a combination of expertise from multiple disciplines. By fostering collaboration and cross-pollination between science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, educators can prepare students to tackle complex problems that transcend traditional boundaries.
For example, the field of bioinformatics, which combines biology and computer science, is revolutionizing our understanding of genomics and personalized medicine. By equipping students with a broad range of skills and knowledge across STEM disciplines, educators can empower them to think critically, solve problems creatively, and adapt to the rapidly changing demands of the future workforce. Interdisciplinary approaches not only enhance the learning experience but also encourage innovation and discovery.
Adoption of Competency-Based Assessment
In the future of STEM education, there is a growing trend towards competency-based assessment, which focuses on measuring students’ mastery of specific skills and knowledge rather than their performance on standardized tests. Traditional assessments often fail to capture the full range of students’ abilities and can be biased against certain groups, leading to inaccurate representations of their proficiency. By shifting towards competency-based assessment, educators can provide a more accurate and comprehensive evaluation of students’ learning outcomes.
Competency-based assessment allows students to demonstrate their proficiency through real-world projects, presentations, and practical tasks that showcase their skills in action. By focusing on mastery rather than memorization, educators can better assess students’ abilities to apply STEM concepts in authentic contexts and prepare them for success in their future careers. Moreover, competency-based assessment provides a more holistic view of students’ strengths and areas for growth, enabling educators to tailor their teaching strategies to meet individual needs.
Investment in Teacher Professional Development
One of the key factors that will shape the future of STEM education is the investment in teacher professional development. Educators play a critical role in preparing students for success in STEM fields, and it is essential that they receive the training and support they need to stay current with the latest trends and best practices in STEM education. By providing opportunities for ongoing professional development, schools can empower teachers to enhance their instructional strategies, leverage new technologies, and create engaging learning experiences for their students.
Professional development programs can take many forms, including workshops, conferences, online courses, and mentorship opportunities. By investing in teacher training, schools can build a strong foundation of STEM expertise within their faculty, ensuring that students receive high-quality instruction that fosters a passion for learning and discovery. Moreover, by fostering a culture of continuous learning and growth among educators, schools can create a dynamic and innovative environment that benefits both teachers and students alike.
Conclusion
As we look towards the future of STEM education, it is clear that the landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing societal needs, and the increasing demand for skilled professionals in STEM fields. By embracing personalized learning, integrating emerging technologies, emphasizing real-world applications, promoting diversity and inclusion, fostering interdisciplinary approaches, adopting competency-based assessment, and investing in teacher professional development, we can create a more equitable, engaging, and effective STEM education system that prepares students for success in the 21st century.
It is essential that we continue to innovate and adapt to meet the evolving needs of the future workforce and ensure that all students have the opportunity to excel in STEM fields. By equipping students with the knowledge, skills, and mindset they need to thrive in a rapidly changing world, we can empower the next generation of innovators, problem solvers, and leaders who will shape the future of STEM education and beyond.




